Health
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Conditions, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, And Treatment
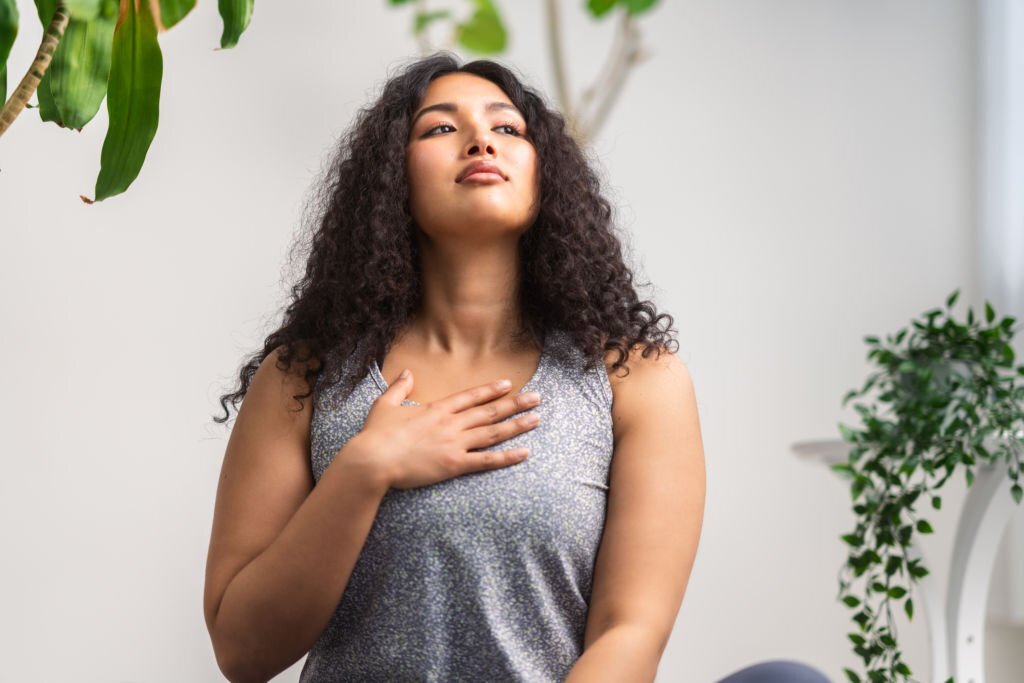


Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) is a persistent inflammatory lung ailment that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include respiratory hassle, cough, mucus (sputum) production, and wheezing. It’s commonly due to long-term exposure to demanding gases or particulate be counted, most usually from cigarette smoke. People with COPD are an improved chance of developing heart disorders, lung cancer, and lots of different conditions.
Emphysema and persistent bronchitis are the two most commonplace conditions that contribute to COPD. These situations usually occur together and might vary in severity among people with COPD.
Causes
Most human beings with COPD are at a minimum of forty years antique and have at least a few records of smoking. The longer and extra tobacco merchandise you smoke, the greater your hazard of COPD is. In addition to cigarette smoke, cigar smoke, pipe smoke, and secondhand smoke can purpose COPD. Your hazard of COPD is even extra if you have allergies and smoke. You can also develop COPD if you’re exposed to chemicals and fumes in the workplace. Long-term publicity to air pollutants and breathing in dust can also motive COPD. In growing countries, at the side of tobacco smoke, houses are frequently poorly ventilated, forcing households to respire fumes from burning gasoline used for cooking and heating.
There may be a genetic predisposition to growing COPD. Up to an anticipated 5 percent of humans with COPD have a deficiency in a protein called alpha-1-antitrypsin. This deficiency reasons the lungs to deteriorate and also can affect the liver. There may be different associated genetic elements at play as well.
Symptoms
At first, you might not have any symptoms. But as the disease gets worse, you might notice these common signs of COPD:
- A cough that doesn’t go away
- Coughing up lots of mucus
- Shortness of breath, especially when you’re physically active
- Wheezing or squeaking when you breathe
- Tightness in your chest
- Frequent colds or flu
- Blue fingernails
- Low energy
- Losing weight without trying (in later stages)
- Swollen ankles, feet, or legs
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, your medical history, and whether you smoke or have been exposed to chemicals, dust, or smoke at work. They’ll also do a physical exam and breathing tests. Let them know if you have an ongoing cough.
The most common test is called spirometry. You’ll breathe into a large, flexible tube that’s connected to a machine called a spirometer. It’ll measure how much air your lungs can hold and how fast you can blow air out of them. Your doctor may order other tests to rule out other lung problems, such as asthma or heart failure. These might include:
More lung function tests
- Chest X-rays which could help rule out emphysema, different lung troubles, or heart failure
- CT experiment, which uses numerous X-rays to create an in depth photograph of your lungs and might tell the health practitioner in case you need surgery or if you have lung most cancers.
- Arterial blood fuel test, which measures how nicely your lungs are bringing in oxygen and taking out carbon dioxide.
- Laboratory tests to determine the cause of your symptoms or rule out other conditions, like the genetic disorder alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency.
Treatment
There’s no cure, so the goal of treatment is to ease your symptoms and slow the disease. Your health practitioner will also need to prevent or treat any complications and improve your average first-rate of existence. One of the quality matters you could do to prevent your COPD from getting worse is to forestall smoking. Talk for your medical doctor about different things you could attempt. Your plan can also encompass:
- Bronchodilators: You inhale these medicines. They help open your airways.
- Combination inhalers: These inhalers pair steroids with a bronchodilator.
- Antibiotics: Your doctor might prescribe these to fight bacterial infections.
- Flu or pneumonia vaccines: These vaccines lower your risk for these illnesses.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: This software includes exercise, ailment management, and counseling to help you stay as healthy and lively as feasible.
- Oxygen remedy: You may need this to reduce shortness of breath, guard your organs, and beautify your first-rate life.
When to See a Doctor?
Talk to your medical doctor in case your signs aren’t improving with treatment or getting worse, or in case you observe symptoms of an infection, which include fever or a alternate in sputum. Seek on the spot medical care if you may’t trap your breath, in case you enjoy extreme blueness of your lips or fingernail beds (cyanosis) or a rapid heartbeat, or if you experience foggy and feature trouble concentrating.

 Model1 month ago
Model1 month agoTiffany Stratton: Biography, Wiki, Age, WWE Career, Net Worth, Before Fame, Boyfriend



 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHow to Send WooCommerce SMS Notifications for Orders





 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months ago7 Essential TikTok Metrics to Track for Higher TikTok Views in 2025


 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoTop 5 Tips for Using File Uploads in Your WooCommerce Store Efficiently

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoWhy Airlines Are Using Virtual Reality Services for Pilot Training



 General1 month ago
General1 month agoThe Hidden Costs of a DUI & How a Lawyer Can Help You Avoid Them





 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoExploring TikTok AI: My Experience Making a Video With Only Artificial Intelligence

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoHow 3D Modeling Transforms AR Experiences for Online Furniture Stores?








You must be logged in to post a comment Login