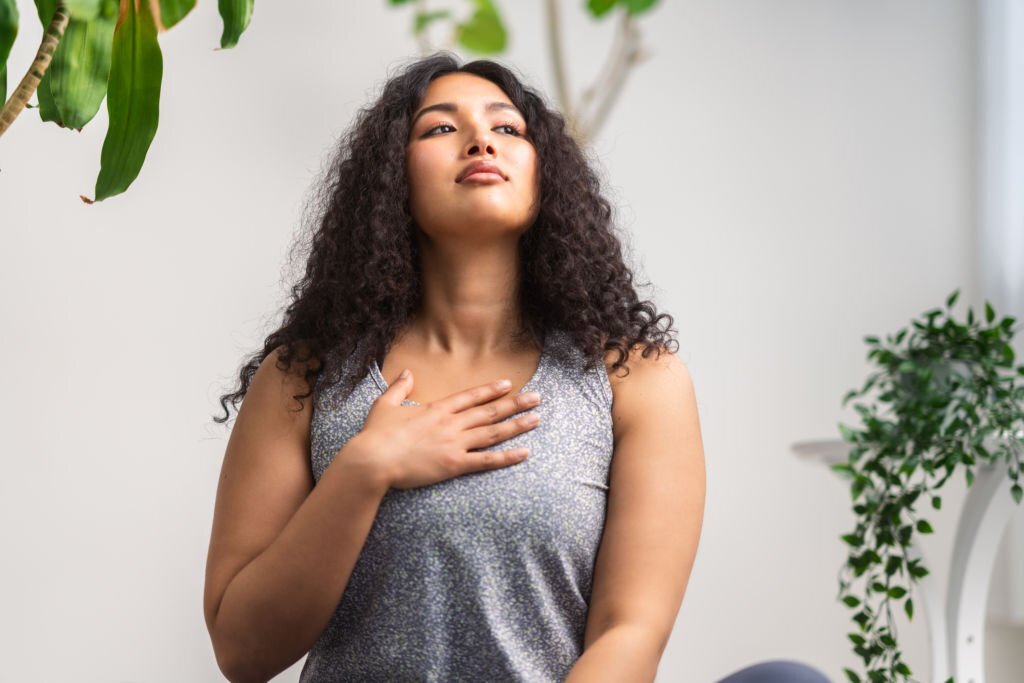

Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a medical condition that restricts blood flow to the heart. It occurs as a result of atherosclerosis, a condition in which the blood arteries that transport blood to the heart muscle tighten and harden. Plaque forms in the arteries because of fat and other substances accumulating in the circulation. Heart failure may occur because of CAD, which causes your heart to beat abnormally. In the long term, it has the potential to develop into heart failure.
The most often reported symptom of coronary artery disease is chest discomfort, generally known as angina pectoris. When discussing cardiac discomfort, the term “chest pain” is often used instead. Squeezing may also be characterized as chest pain, heaviness, tightness, pressure, hurting, burning, numbness, fullness, or squeezing, among other things. The source of the problem is often thought to be indigestion or heartburn, however, this is not the case. Angina is most often linked with chest pain, although it may also cause discomfort in the left shoulder blade and arms, as well as the neck, back, and jaw.
CAD symptoms include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, weakness, sweating, nausea, and other signs and symptoms such as heart palpitations. Making adjustments to one’s lifestyle, such as decreasing physical activity and stress, may help manage stable angina more successfully. The following are some other ways to treat stable or unstable angina:
Atherosclerotic narrowing in males who are below 55 years and females who are below the age of 65 is referred to as premature coronary artery disease. This is asymptomatic in most instances; however, symptoms such as heart attack or angina are also linked with this condition.
Following are the CAD symptoms along with their causes:
Shortness of breath: If your heart is unable to pump enough blood to satisfy your body’s requirements, you may experience shortness of breath or severe fatigue.
If you have any risk factors for CAD, such as high blood pressure or excessive cholesterol, see your doctor. If you have diabetes or obesity, or if you have a significant family history of heart disease, you should also visit your doctor. If you have signs or symptoms of constricted arteries, your doctor may recommend that you get tested for CAD.
If you are suffering from persistent angina or other signs of coronary artery disease, make an appointment with a healthcare expert as soon as possible. Suffocation (even if not physically involved) and palpitations are medical emergencies that need urgent medical attention. This is particularly true if they coexist with other signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD).
If you see any of these symptoms, contact your local emergency services right once. Do not disregard any of the warning signs and symptoms of CAD. Individuals often postpone getting medical attention because they are unsure whether or not anything is really wrong.
As a result, it is conceivable that treatment may be delayed at a time when you are most vulnerable. If you suspect you are suffering a heart attack or have other symptoms of CAD, you should seek medical attention as quickly as possible. The sooner you seek treatment for a heart attack, the better your chances of survival.
Sick of customers missing critical order updates in their clogged inbox? The answer is easy:…
The construction world is evolving by adopting the newest technology in the guise of Artificial…
Browsing an online shop only to halt instantly as a product animates on the screen.…
Assume this: you're standing in line at a café. The person ahead of you pulls…
Demands from work, family, and social commitments can feel never-ending, which means self-care is often…
Making your home more modern while achieving a refreshed look exists without the necessity of…